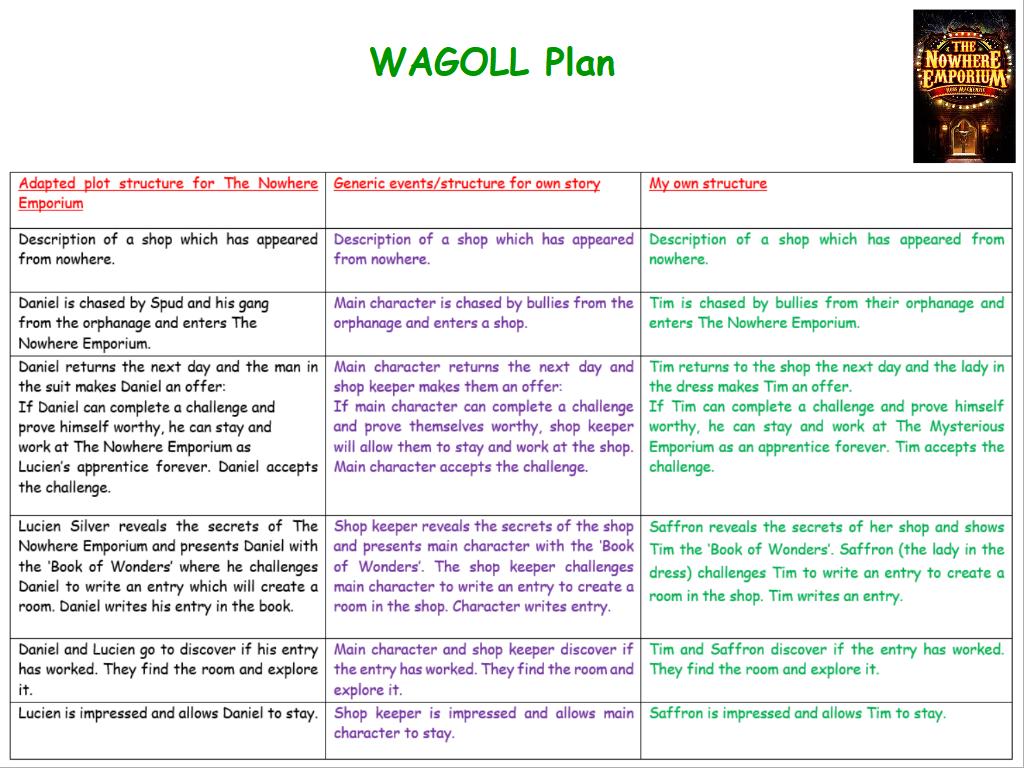
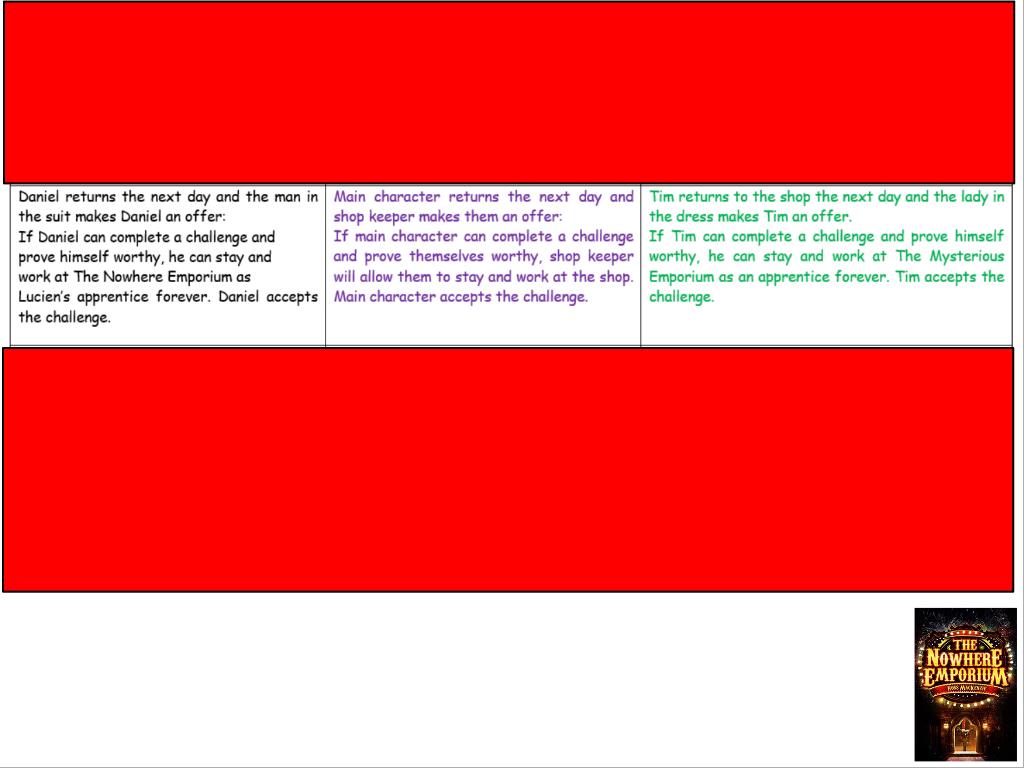
Monday
Monday 6th October
Copy the sentences and add semi-colons to separate main clauses.
-
I have a meeting tomorrow I’m not sure if it will be in person or online.
-
She loves classical music her brother prefers jazz.
-
I have a big test tomorrow I can’t go out tonight.
-
The cake was delicious everyone asked for a second slice.
-
Some students studied for weeks others waited until the last minute.
-
He didn’t see the warning sign he drove into the restricted area.
-
The sun was setting the sky turned shades of orange and pink.
06.10.25
LC: To identify prime numbers
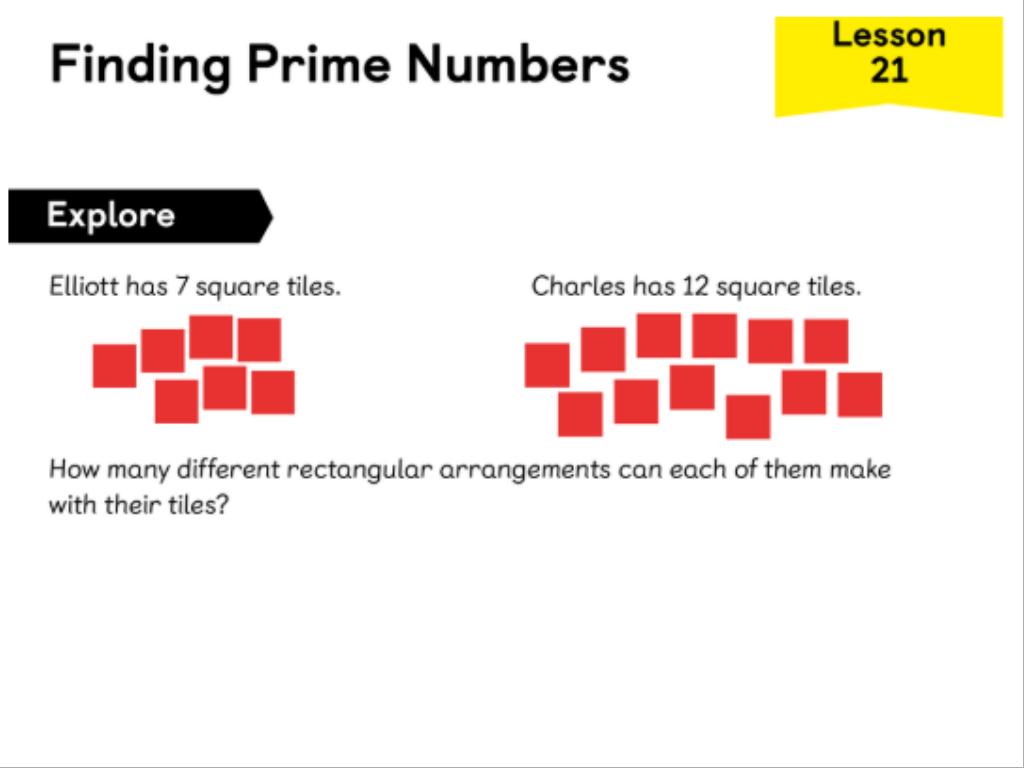

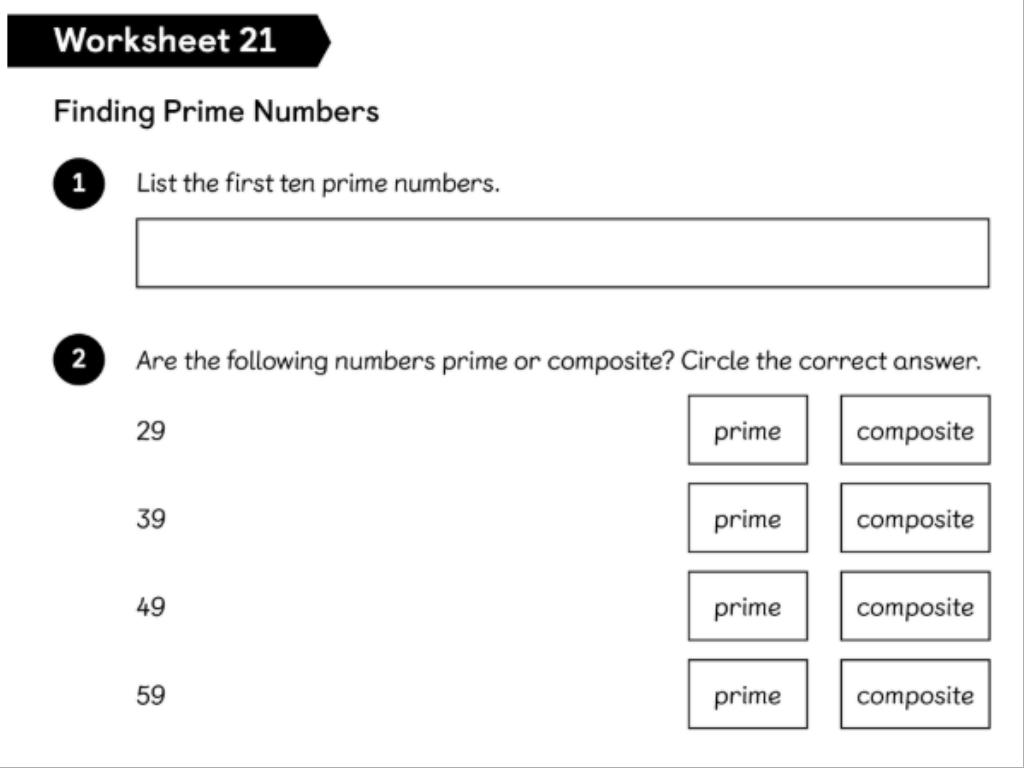

Monday 6th October
LC: To write the next part of your story using action, dialogue and description.


The classroom buzzed with quiet excitement as Mr Patel placed a mysterious box on his desk. It was wooden, carved with strange patterns, and locked with a heavy brass clasp.
“You’ll each get a turn to guess what’s inside,” he announced with a smile.
Ellie leaned forward, her eyes wide. The box seemed to hum faintly, as if it were alive. She shivered but couldn’t look away. What could be inside? A puzzle? A treasure? Or something else entirely?
Questions
Retrieve
What was the box made of?
Interpret
How do the children feel about the box? Use evidence from the text.
Choice
Why does the author describe the box as “humming faintly”?
Monday 6th October
LC: To retrieve information from a text.
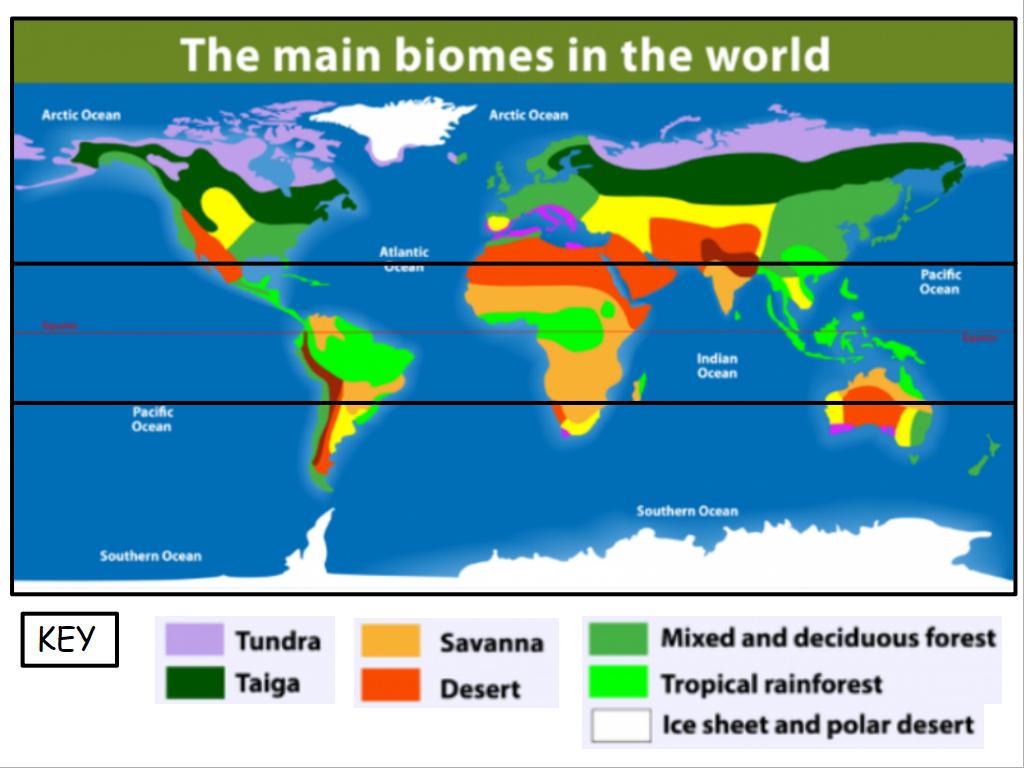
Deciduous Forest Biome Fact File
What is a Deciduous Forest Biome?
A deciduous forest biome contains trees that lose their leaves every year. They grow in areas that have four seasons with cold winters and hot, wet summers. The changes in climate trigger the deciduous trees to transform. During autumn, the colours of the leaves change from green, to brown, to orange and yellow. When winter arrives, the trees have usually dropped all of their leaves and have empty branches.
Where are Deciduous Forest Biomes?
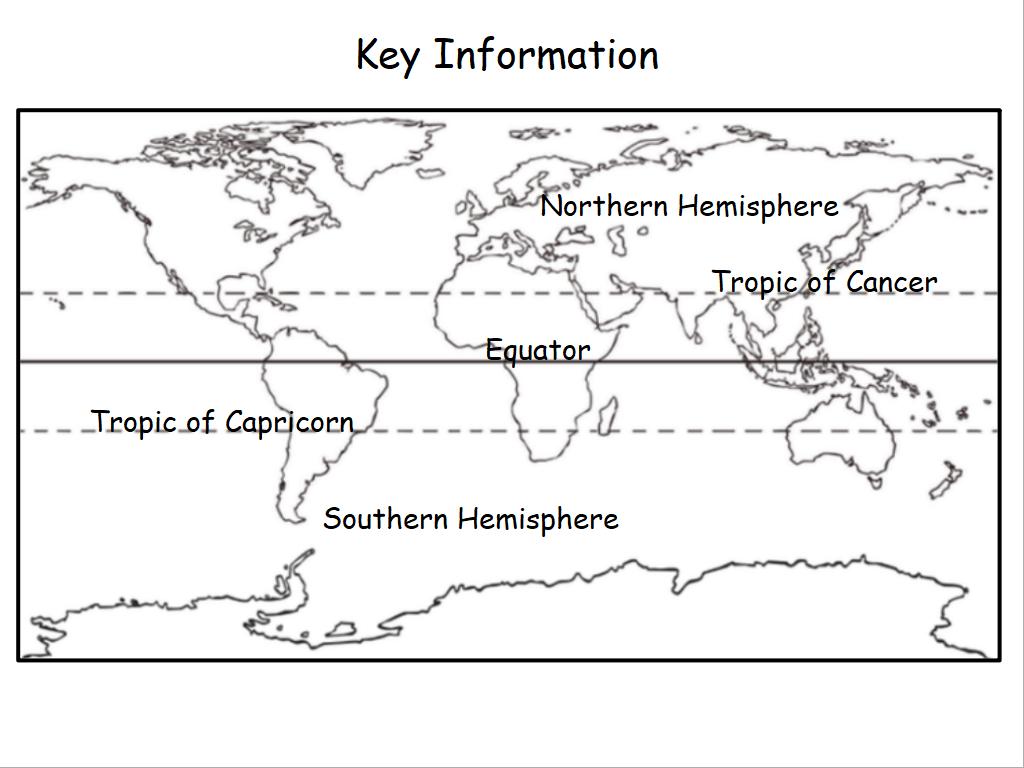
Deciduous forest biomes are found between the polar regions and the tropics.
How Have Plants Adapted to Living in Deciduous Forest Biomes?
When trees in deciduous forest biomes drop their leaves it helps them to save energy and keep water throughout the harsh winters. They are able to cut off the supply of water to their leaves and seal off the area between the leaf stem and tree trunk. Deciduous trees then enter a period of dormancy or sleep. They have thick bark that protects them from the cold weather. Many plants are able to use their sap to stop their roots freezing.
During spring and summer, deciduous trees flower and grow. They produce thin, broad and lightweight leaves that might be star, heart or oval shaped. Their leaves help them to absorb sunlight to make food. Some trees can grow fruits and nuts. Examples of deciduous trees include willow, ash, horse chestnut, elm, maple and birch.
The deciduous beech is Australia’s only cold-climate, winter deciduous tree. It is only found in Tasmania. Most trees that are native to Australia are evergreen. The deciduous beech is found in highland and mountainous areas that receive lots of rainfall. During winter, it drops its leaves to protect itself from frost and snow and to save energy. The dropped leaves return minerals to the soil for the next spring growth. Deciduous beech trees are slow and low-growing. Their seeds do not travel far as they have no adaptations for wind dispersal.
Oak trees have adapted to be able to live in areas with little water and nutrition. They have a taproot that goes deep into the ground to access water. Oak trees also have huge roots that go sideways. They spread far from the trunk and help the tree to stay in place during strong winds. Oak trees have a thick, solid bark that is like armour and protects them from the heat of fires. After a fire, they are able to form new seedlings quickly that grow fast. Oak trees make nuts called acorns that have seeds inside. They are heavier than most seeds and are carried away by animals like squirrels. Acorns begin to germinate very soon after falling from an oak tree
How Have Animals Adapted to Living in Deciduous Forest Biomes?
Animals such as bears, racoons, wood mice and deer live in deciduous forest biomes. They have a range of adaptations like sharp claws and strong tails to help them to climb trees. Some animals migrate during the winter and some hibernate or go into torpor. Others store food during the warmer seasons that keeps them alive throughout winter. They might put nuts and seeds into the hollows of trees or bury them in shallow holes. Some of these seeds sprout and grow into plants.
Squirrels are excellent climbers which helps them to reach food and keep away from predators. They can rotate their back paws by 180° so that they point backwards. This allows them to grip tree bark from the reverse and go down trees headfirst. Their soft, fleshy pads on the soles of their feet and sharp claws also assist with their climbing and grasping. Squirrels have large eyes that allow them to see when there is not much light. Some have special hairs on their heads and limbs that improve their sense of touch. Squirrels are able to communicate with each other and provide warnings about predators.
Skunks have some useful ways to defend themselves from predators. Their black and white striped fur and sharp teeth provide a warning for other animals to stay away from them. Skunks are able to spray a musk that smells very bad from two glands near the base of their tail. The musk is a thick, yellow liquid. It can temporarily blind predators and allow the skunks to get away to safety. Skunks are nocturnal which protects them from daytime predators and also means that they do not waste energy when it might be too warm. They are good at digging and usually live in dens. Skunks may enter a state of torpor for several days when the weather gets very cold. They are omnivores and can eat different food depending on what is available.
Questions:
1. What does it mean when a tree is deciduous?
2. How many seasons do deciduous forests have?
3. What happens to the leaves of deciduous trees in autumn?
4. Where in the world are deciduous forest biomes typically found?
5. Why do deciduous trees drop their leaves in winter?
6. What protects deciduous trees from cold weather?
7. Name three types of deciduous trees mentioned in the text.
8. Where is the deciduous beech tree found?
9. How do oak trees protect themselves from fires?
10. What do oak trees produce that contains seeds?
11. How do squirrels use their back paws to help them climb trees?
12. What special ability do skunks have to defend themselves from predators?
13. Why are skunks mostly active at night?
14. Name two ways animals in deciduous forests survive the winter.
15. What happens to the leaves that fall from deciduous trees in winter?
Monday 6th October