Monday 8th December 2025
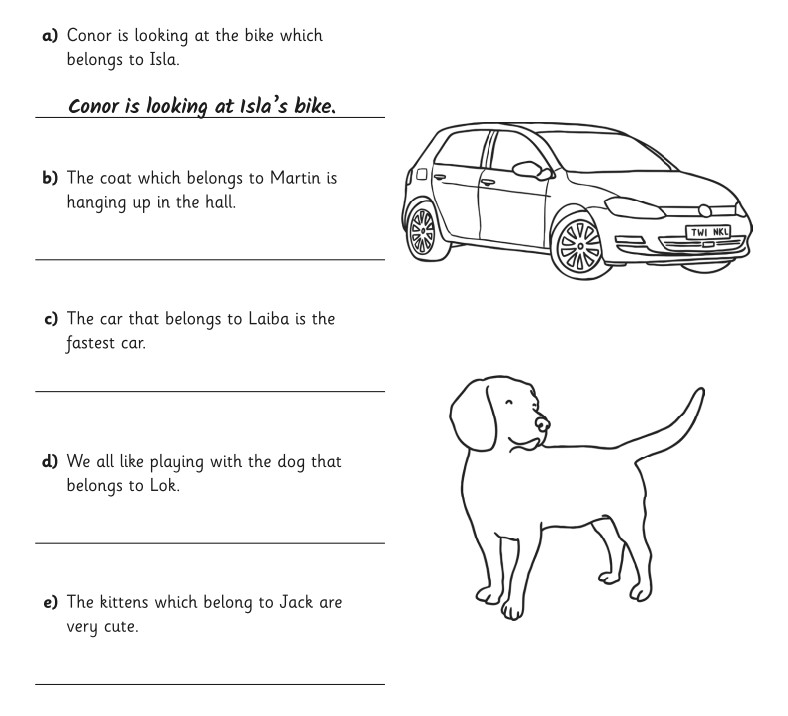
This text is a scene from the film Encanto.
 R
R
What colour was the glow from the shard carried by the rat?
I
Use evidence from the text to explain what might happen next.
C
How does the author show that Mirabel thinks there could be something dangerous on the other side of the painting?
Monday 8th December 2025
LC- Prepare a poem to read aloud using intonation, volume and action.
Follow this poem while I read it aloud and we will discuss each part.


A summary
‘Leisure’ by William Henry Davies is about the importance of making time for noticing and connecting with nature
The poem begins with some examples of what we can do to take the stress out of our body. Sometimes, instead of rushing around all of the time, we need to keep things simple and just stop and appreciate what is around us.
We are going to prepare to perform the poem with intonation, volume and appropriate actions.
First of all, work with your partner. Think about the words, look at the punctuation and think about what actions you might use.
Now share!
Adapted
Learn the poem

Monday 8th December 2025.
LC: To create sentences with fronted adverbials for when.
Chunk 5 focusses on Suleiman’s arrival on a magic carpet.
You will be focusing on how the magic carpet moves and collecting vocabulary to describe the carpet's movements.


Task: Orally rehearse chunk 5 which includes vocabulary to describe the magic carpet and fronted adverbials for when and write this paragraph in your book using the teacher model.
08.12.25
LC- To multiply 3 digit numbers.
Model
437 x 4 =
790 x 5 =
Your turn
636 x 3 =
728 x 2 =
901 x 7 =
826 x 8 =
400 x 9 =
Monday 8th December 2025
LC: To identify when evaporation and condensation take place in the water cycle and explain the rate of evaporation with temperature.

Recap:
What is the water cycle?
Water on Earth is recycled over and over again; it’s always moving. It is this recycling process that we call the water cycle.
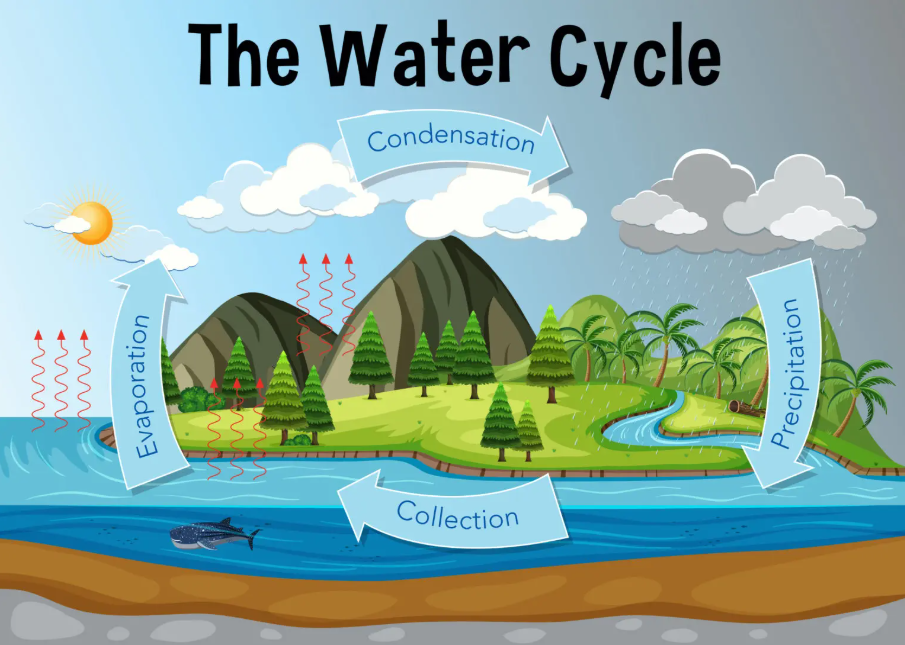
1. Evaporation – water evaporates into the air
The sun heats water on land, rivers, lakes and seas and turns it into water vapour.
The water vapour rises into the air.
2. Condensation – water vapour condenses into clouds
As water vapour in the air cools down, it turns back into tiny drops of water. These tiny drops of water form clouds.
3. Precipitation – water falls as rain
As the amount of water vapour in the clouds increases, the clouds get heavier and heavier. Water falls back to the ground as rain, sleet, or snow if it’s cold enough.
4. Water returns to the sea
As rainwater runs over the land back to rivers and the sea, some is taken up by and used by plants, and some returns to the air through transpiration. Most rainwater collects in lakes or rivers and flows back to the sea for the water cycle to start again.
Task:
We will be making a mini water cycle model and observing water evaporating and condensing inside the bag.
How to instructions:
Can you make a water cycle in a bag? Draw the sun and a cloud on a bag. Add some water and stick it to the inside of a sunny window. Watch as the water evaporates and condenses inside the bag!

What do you think will cause the water to evaporate?
In your books explain the role of evaporation and condensation in the water cycle.
Explain if you think the water will evaporate faster or slower depending on the temperature.
Adapted
When Do Evaporation and Condensation Take Place in the Water Cycle?
Evaporation
-
What it is: Evaporation is when liquid water changes into water vapour (a gas).
-
When it happens:
-
When the Sun heats up water in rivers, lakes, oceans, puddles, or even soil and plants.
-
Warm water particles gain energy, move faster, and escape into the air as vapour.
-
Condensation
-
What it is: Condensation is when water vapour cools and changes back into liquid water.
-
When it happens:
-
As warm, moist air rises, it cools down in the atmosphere.
-
The water vapour loses energy and turns back into tiny water droplets.
-
These droplets form clouds, and when they join together and grow heavy, they fall as rain, snow, or hail (precipitation).
-
How Temperature Affects the Rate of Evaporation
-
Higher temperature → faster evaporation
-
They move faster,
-
They escape from the water surface more easily,
-
So water evaporates more quickly.
-
-
Lower temperature → slower evaporation
Examples
-
A wet towel dries faster on a hot sunny day than on a cool day.
-
Puddles disappear sooner in the summer than in the winter.
antarctica primary picture news resource england 8th december.pdf