Friday 16th January
LC: To identify basic examples of human rights.

Basic human rights are rights and freedoms that every person in the world is entitled to, simply because they are human. These rights are universal, meaning they apply to everyone, everywhere, regardless of their nationality, race, religion, or any other status.
Below are some of the main human rights:
Right to Life- Everyone has the right to live and to be free from harm.
- You have the right to think freely, have your own beliefs, and practice your religion.
Freedom of Expression
- Everyone has the right to express their thoughts and opinions.
Right to Education
- Everyone has the right to go to school and receive an education.
- Everyone has the right to privacy in their personal life and family.
Freedom of Movement
- Everyone has the right to move freely within their country and to leave and return to their country.
Right to Work and Fair Conditions
- Everyone has the right to work and to fair working conditions.
Right to Health
- Everyone has the right to the highest attainable standard of physical and mental health.
Let's look at children's rights below.
Can you spot any that are similar to the basic human rights?

Whole Class Discussion
Let's select some rights and discuss why they are important!
Are there any rights that you don't understand?
Friday 16th January 2025
LC: To express time using adverbs.
Let's take a look at our explanation booklet. What have we completed?
Today we are going to write the fourth and the fifth paragraph. We are also going to sketch and label a flower.
Look at your plans. What will you be writing about today? I will look at the next stages on my plan!
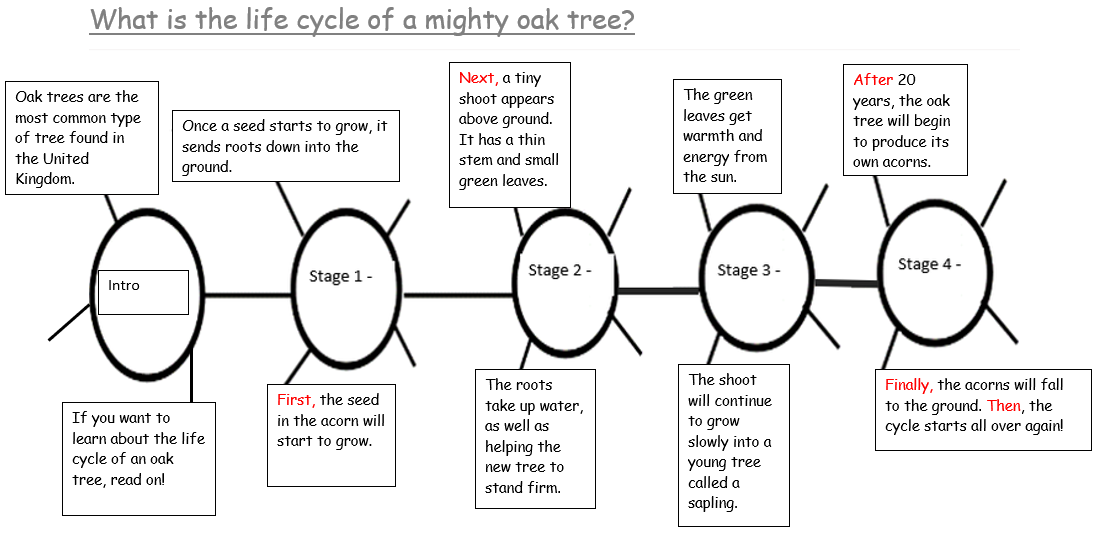
Before we begin writing, we need to look at our success criteria on our learning wall! What do we need to include?
What we need on each page!
Page 1 - Heading and a picture of a plant.
Page 2 - Introduction.
Page 3 - Subheading (Germination) and paragraph one.
Page 4 - Subheading (Growing and Flowering) and paragraph two.
Page 5 - Subheading (Pollination) and paragraph three.
Page 6 - Subheading (Fertilisation and Seed Formation) and paragraph four.
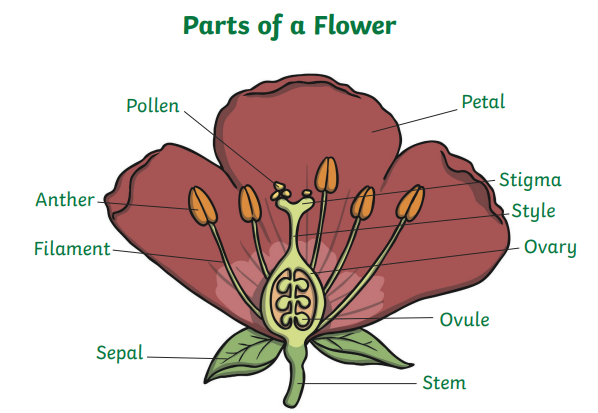
Page 7 - Labelled diagram of a flower (image below).
Page 8 - Subheading (Seed Dispersal) and paragraph five.