Monday
Monday 2nd December
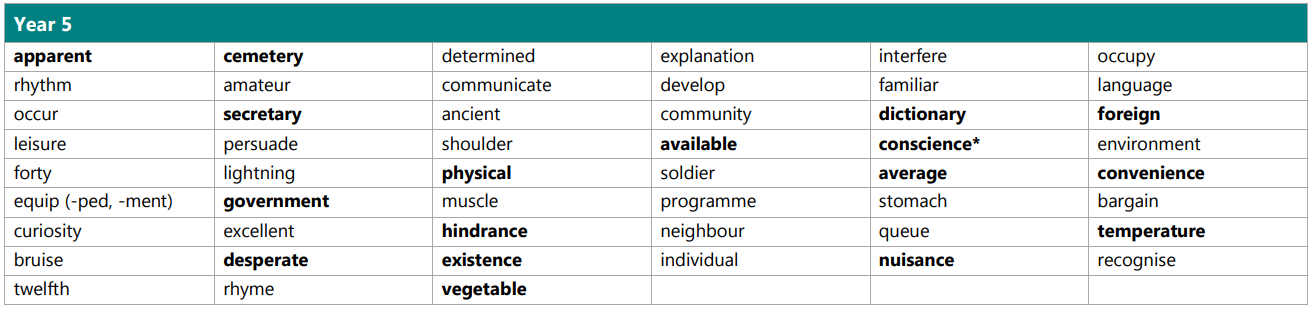
Edit the adjective in each sentence to change the description of the noun.
1) The old man walked down the street.
2) Sarah avoided the red chair.
3) Aaron was playing with a bouncy ball.
4) The grumpy child sat in the corner.
5) Henry walked down the straight line.
6) John tried a spicy pepper.

Monday 2nd December
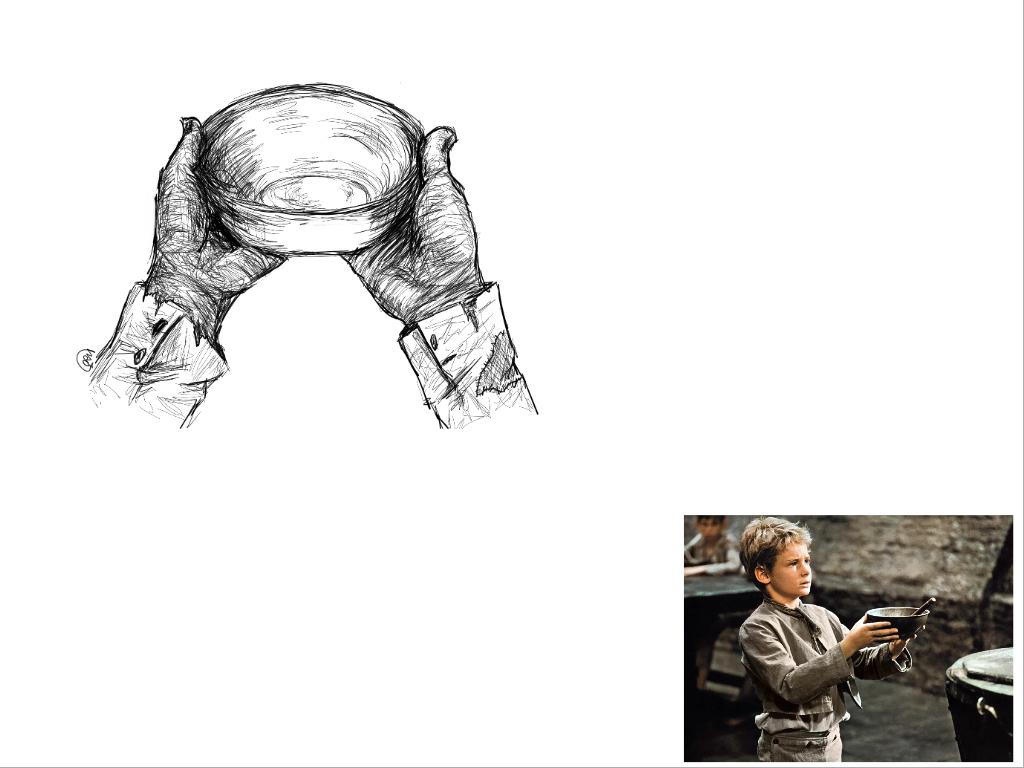
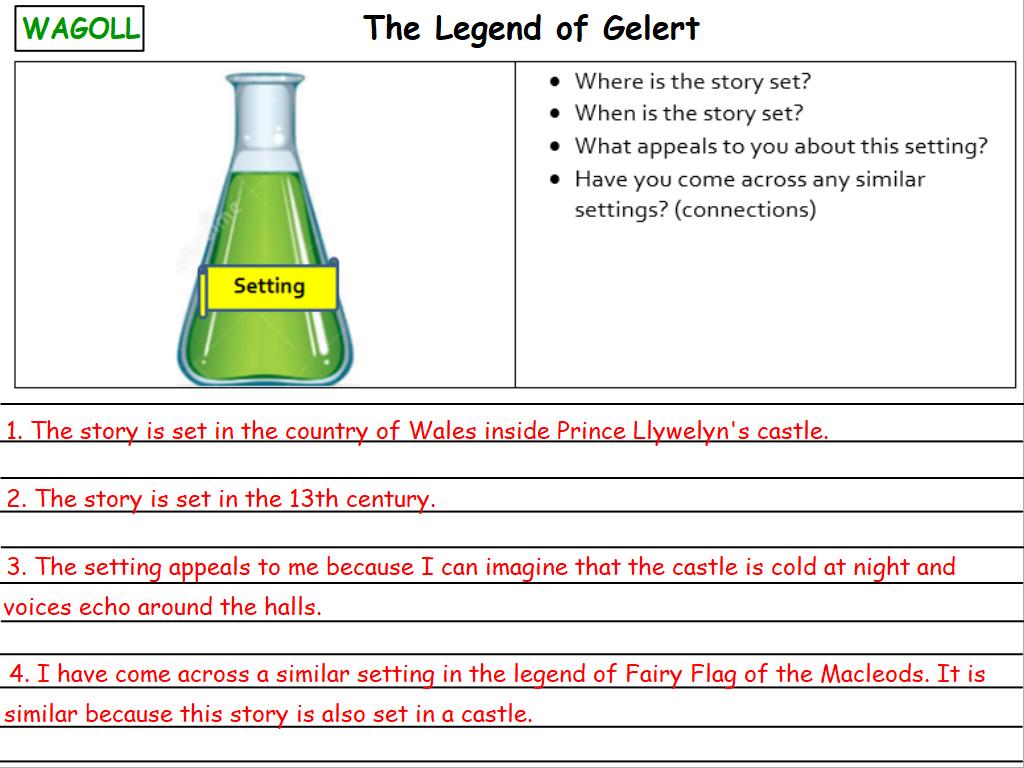
LC: To explore the setting and characters within a text.














02.12.24
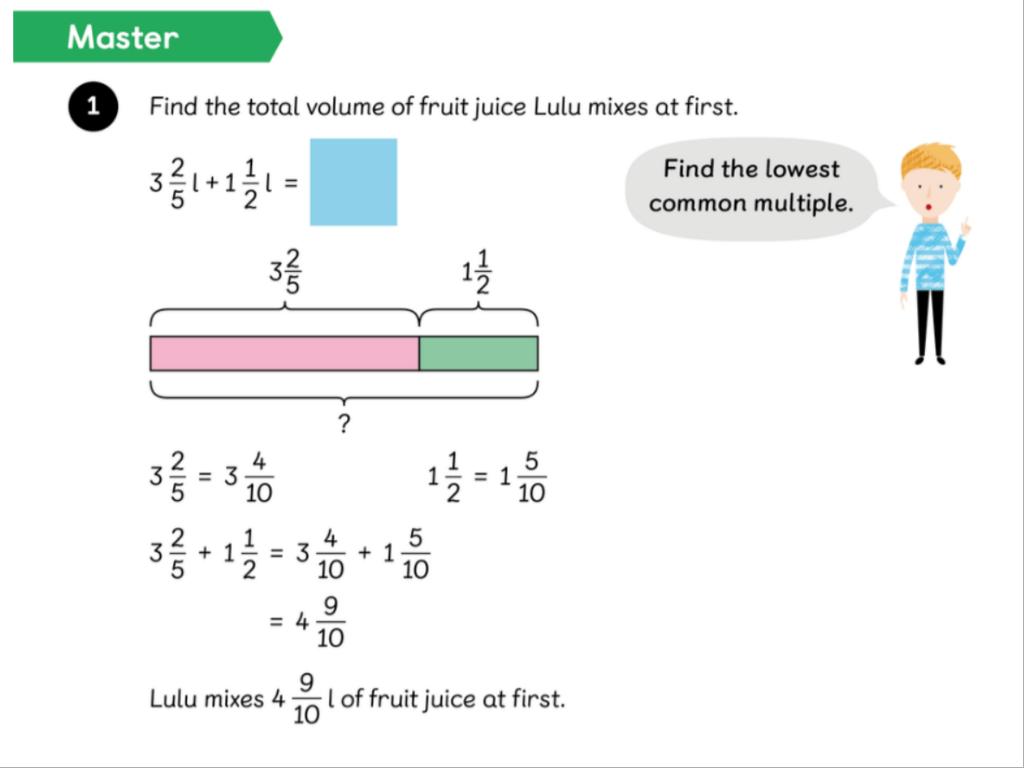
LC: To be able to add and subtract fractions with different denominators and mixed numbers.

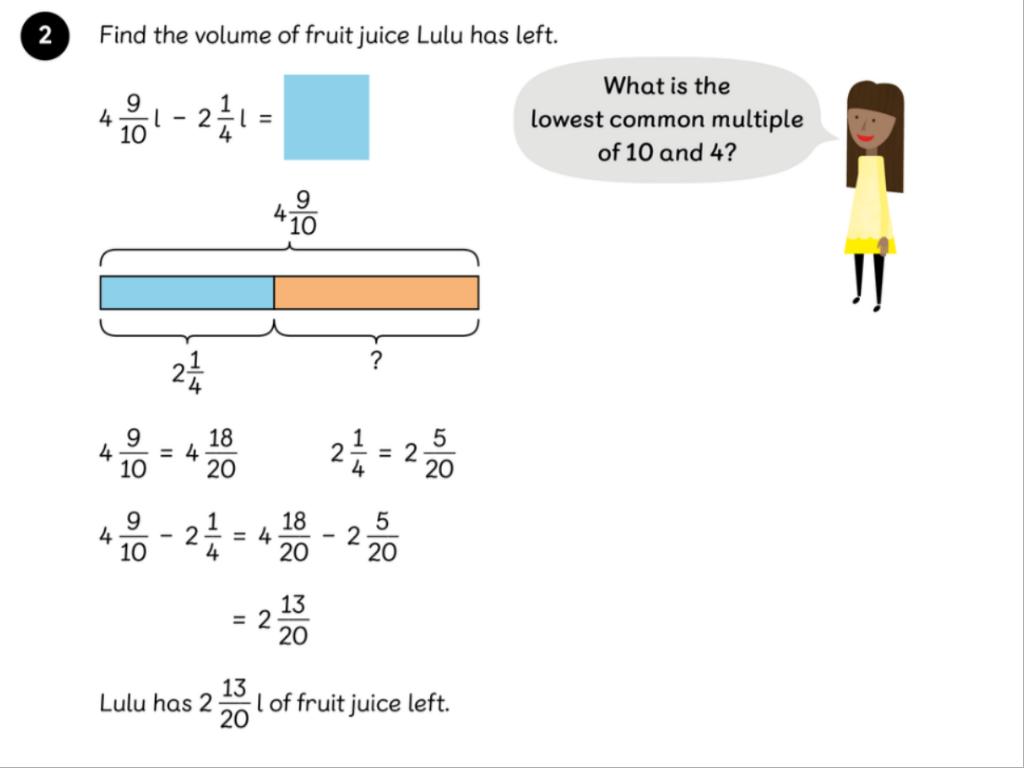


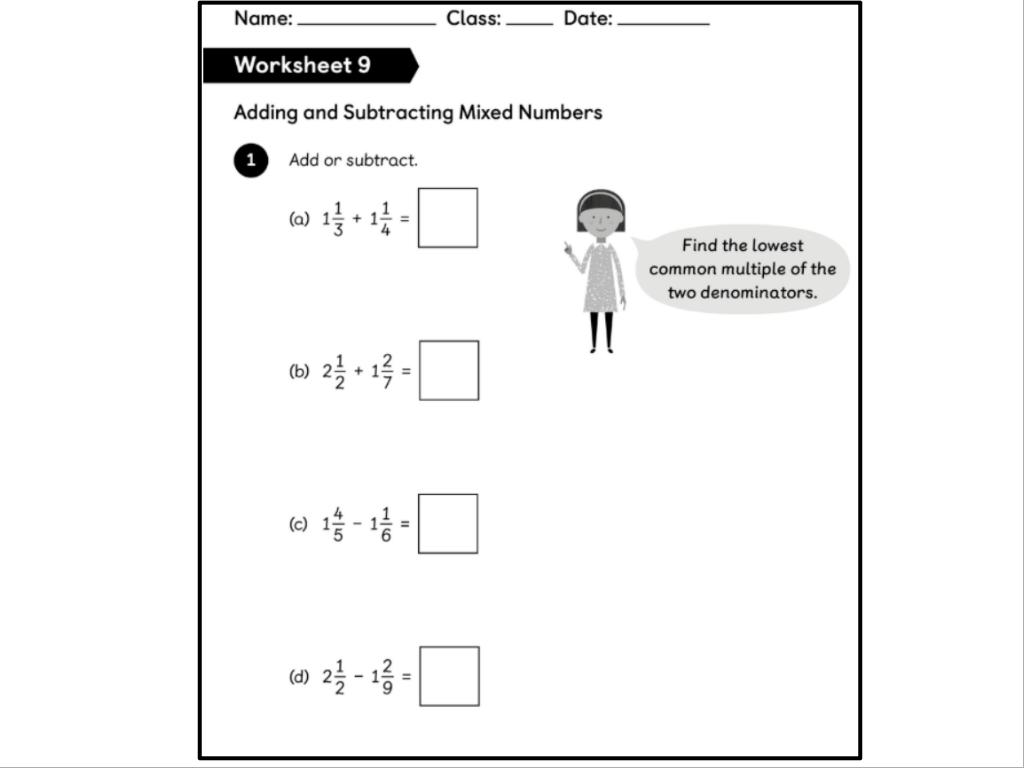
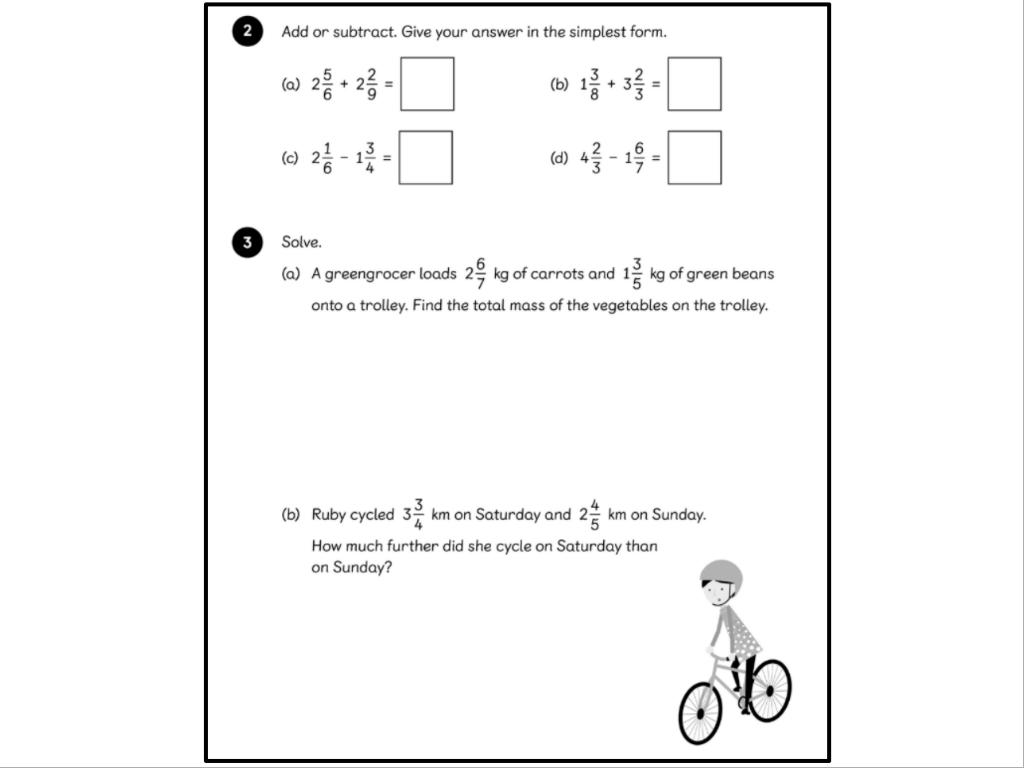








https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/p018rzdg
https://www.bbc.co.uk/teach/class-clips-video/articles/z78xy9q
1. Faster Transport of Goods
Before railways, goods were moved by horses, carts, or slow boats. Trains made it much quicker to transport raw materials like coal and iron to factories, and finished goods to markets.
2. Bigger Loads
Trains could carry much heavier loads than horses or carts. This meant factories could get more materials and sell more products, helping businesses grow.
3. Better Connections
Railways connected towns, cities, and ports. This made it easier for industries in one place to trade with other places, even far away.
4. Encouraged New Factories
With railways making transportation easier, people started building factories near railway lines, creating jobs and boosting the economy.
5. Cheaper Goods
Because railways made transport faster and cheaper, goods became less expensive to make and sell. More people could afford to buy them.
6. Helped Mining and Farming
Industries like coal mining and farming also benefited. Railways carried coal to power the factories and food to feed the workers, improving life for many.
In short, railways made everything faster, cheaper, and better connected, helping industries grow and changing the way people lived and worked!