Wednesday
Everyone on TTRockstars!

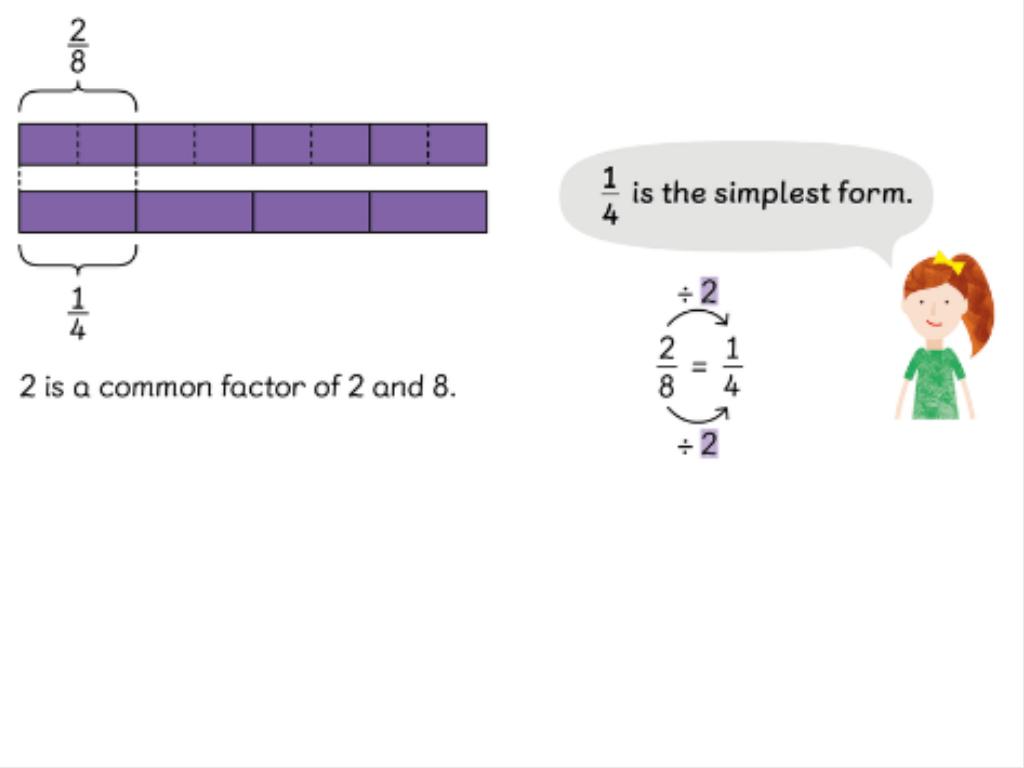



/i/video/Year_6/Who_was_Charles_Darwin____History_in_a_Nutshell___Animated_History.mp4

R - What animals find shade under rocks and in holes?
I - Does it rain in Texas? Explain.
C - Find a word that means the same as 'banned'.
Wednesday 13th November
LC: To use scanning and close reading strategies to locate information.
Charles Darwin
Charles Robert Darwin was a famous naturalist (an expert in studying nature). He was best known for his work on the theory of evolution and his idea of natural selection.
Early Life
Charles was born on the 12th of February 1809 in Shrewsbury, Shropshire into a wealthy family. His father was a doctor and his mother was the daughter of a famous pottery producer. Charles’s grandparents were both heavily involved in a movement called the Enlightenment which encouraged the idea that people should think for themselves without being ruled by authority or religion.
Following in the footsteps of his father, Charles began to study medicine at the University of Edinburgh. However, he soon realised that this was not the career for him and moved to Cambridge to train for a job within the church. He was especially interested in natural history and he was offered the chance to travel the world as a guest naturalist.
HMS Beagle
In 1832, Charles embarked on an exploratory world voyage on board the HMS Beagle which lasted for almost five years. It was his job to make notes about the animals, plants and geology of the countries that he visited. Charles explored a wide variety of countries and he encountered numerous new species on his travels.
The Galápagos Islands
Charles travelled to the Galápagos Islands: a group of 19 islands and many smaller islets in the middle of the Pacific Ocean. When he was there, he noticed species which were similar but with small differences. For example, he noticed that the birds that he saw on some of the islands were slightly different, even though they lived only a few miles apart. Charles began to realise that these birds were once the same species. After spending a long time apart from others, the birds had begun to evolve (adapt and change over time) to suit their surroundings.
He believed that this was because those animals which were better suited to their surroundings lived longer and produced more offspring. These offspring had the same traits as their parents and the species would gradually change over a long time. He called this process ‘evolution by natural selection’. Following this voyage, Charles started to notice examples of natural selection throughout the world.
‘On the Origin of Species’
Charles was worried that his idea of evolution by natural selection would be controversial and groundbreaking. The Christian religion teaches people that God created everything but Charles’s theory of evolution challenged that idea. Therefore, Charles decided that he needed to gather more evidence before he introduced his ideas to the world.
In November 1859, Charles published all of his research in his book ‘On the Origin of Species by Natural Selection’. ‘On the Origin of Species’ (as it is commonly known) was an international bestseller. He updated the book many times and, later, introduced the phrase ‘survival of the fittest’ as a replacement for ‘natural selection’ in the book.
Charles went on to write another book, ‘The Descent of Man’, where he suggested that humans may have evolved from another species. Even though Darwin had no fossil evidence at the time to prove this idea, modern scientists generally agree that humans share a common ancestor with apes, such as chimpanzees and gorillas.
Charles's Legacy
Recent scientific studies have proven that Charles’s theory of evolution was accurate. Even though over 100 years have passed since Charles first published his books, his ideas are still talked about today. His theory of evolution was hugely important and changed the way that scientists view the world.
Glossary
ancestor: An early type of animal or plant from which a later, usually different, type has evolved.
evolution: The idea that all living things are descended from creatures which have slowly changed over millions of years.
geology: The study of the earth and how it has changed over time.
naturalist: An expert in natural history. traits: A quality that makes one living thing different from another.
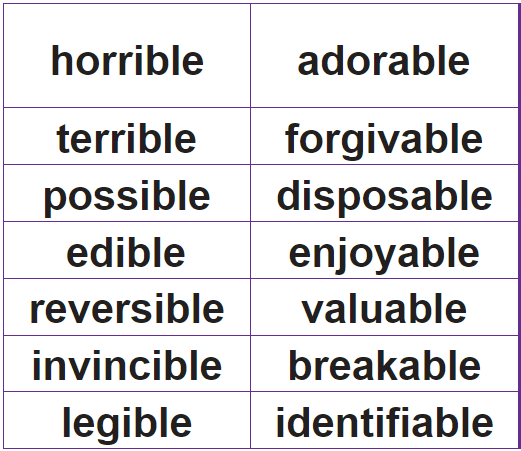
TASK



Notes:
- ‘-able’ is more common than ‘-ible’.
- The ‘-able’ ending is usually used (but not always) if a complete root word can be heard before it. In some cases the ending of the root word may change, for example, rely/reliable.
- The ‘-ible’ root is common if a complete root word cannot be heard before it (but not without exception, for example sensible).
- The ‘-able’ ending is used if there is a related word ending in ‘-ation’, for example, applicable/application.
When you add ‘-ibly’ or ‘-ably’, the same conventions apply as above, but you drop the ‘e’ from the end of the word before adding ‘-ibly’ or ‘-ably’.